- Home
- About Us
- Products
-
Heat-Pump Dehumidifier DeAir
 DeAir.RE
DeAir.RE -
Heat-Pump Dryer DeAir.RE-H
 DeAir.RE-H
DeAir.RE-H -
Heat-Pump Stainless Steel Dehumidifier
 DeAir.RE-INOX
DeAir.RE-INOX -
Heat-Pump Isothermal Dehumidifier DeAir.CRE
 DeAir.CRE
DeAir.CRE -
Dezenno Dehumidifier
 Dezenno
Dezenno -
Heat-Pump Ceiling Mounted Dehumidifier DeAir
 DeAir.RE-CL
DeAir.RE-CL -
Dehumidifier Olmas
 Olmas-OS
Olmas-OS -
Industrial Humidifier DeAir
 DeAir.HM
DeAir.HM -
Heat-Pump Dryer Daxwell
 Daxwell
Daxwell -
Electric Duct Heater DeAir
 DeAir.Heat
DeAir.Heat -
Air Handling Unit Dezenno.MAX
 AHU
AHU
-
- Services
- Projects
- Warranty – Maintenance
- News
- Contact
Industrial Vegetable and Fruit Dryers: Optimal Solutions to Elevate Vietnamese Agricultural Products
26/06/2024
Industrial Vegetable and Fruit Dryers: Optimal Solutions to Elevate Vietnamese Agricultural Products
In the context of modern agriculture continuously seeking solutions to enhance value and extend the shelf life of agricultural products, industrial vegetable and fruit drying technology plays a pivotal role. Drying not only transforms fresh produce into crispy, easy-to-preserve dried products with only about 10% moisture content, but also unlocks export potential and product diversification. This is an indispensable solution for agricultural processing enterprises, cooperatives, and factories looking to optimize production processes, minimize spoilage, and enhance the competitiveness of their products in the market.
Superior Benefits of Applying Industrial Vegetable and Fruit Dryers
Investing in industrial dryers brings outstanding economic and quality value to agricultural businesses:
- Enhance Product Value: Transform fresh vegetables and fruits into high-quality dried products, meeting diverse market demands, from ready-to-eat snacks to processed ingredients.
- Extend Preservation Time: Reduce moisture content to a safe level (around 10%), completely inhibiting the growth of microorganisms and mold, allowing products to be stored for a very long time without chemical preservatives.
- Retain Nutrients and Natural Color: Heat Pump drying technology and heat pump dryers operate at low temperatures, preserving maximum vitamins, minerals, flavor, and original color of vegetables and fruits.
- Optimize Productivity and Costs: Large-capacity dryers with precise temperature and humidity control ensure fast, uniform drying, saving energy and reducing labor costs.
- Ensure Consistent Quality: Industrial drying enables strict control of parameters, ensuring every batch meets the highest quality standards, thereby enhancing brand reputation.
Efficient Industrial Vegetable and Fruit Drying Process
To optimize the efficiency of industrial vegetable and fruit drying, adhering to a standard process is crucial:
1. Raw Material Preparation – Standardization and Uniformity
Incoming raw materials must be carefully selected, ensuring freshness and no damage. Then, wash thoroughly using a specialized water treatment system to remove impurities. Cutting vegetables and fruits into uniform pieces is a key factor directly affecting drying time and the quality of the final product. In factories, industrial cutting machines are used to ensure precision and productivity.
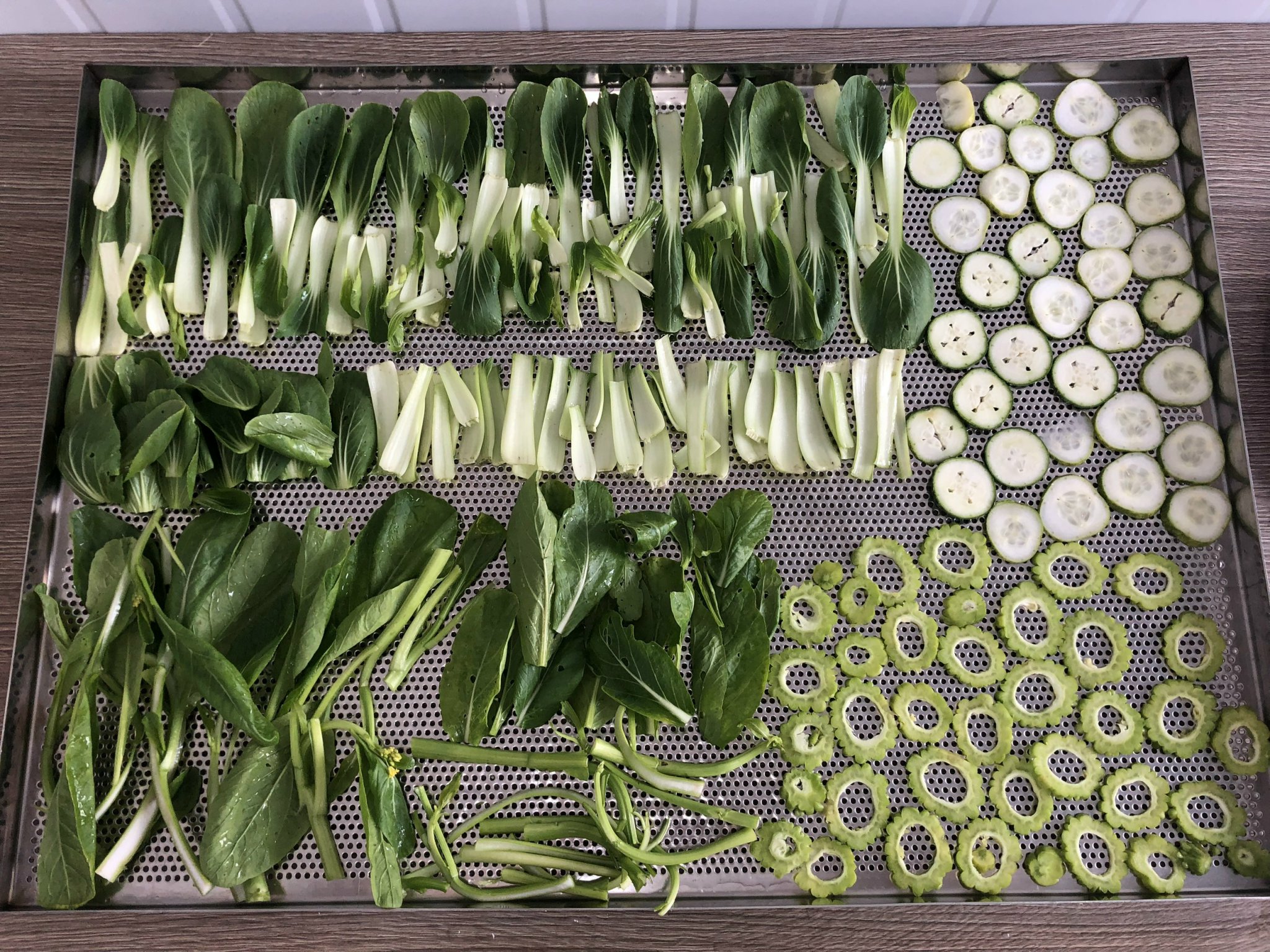

2. Pre-treatment (Blanching) – Enzyme Deactivation and Enhanced Rehydration
Blanching is an indispensable step to deactivate enzymes, preserve color, flavor, and reduce drying time. For industrial scale, automatic or semi-automatic blanching systems are used, ensuring precise temperature and blanching time for each type of vegetable and fruit:
- Water Blanching: Use large blanching tanks with automatic temperature control systems, ensuring all vegetables are blanched uniformly.
- Steam Blanching: Industrial steam heating systems are designed for optimal steam circulation, allowing vegetables to soften quickly.
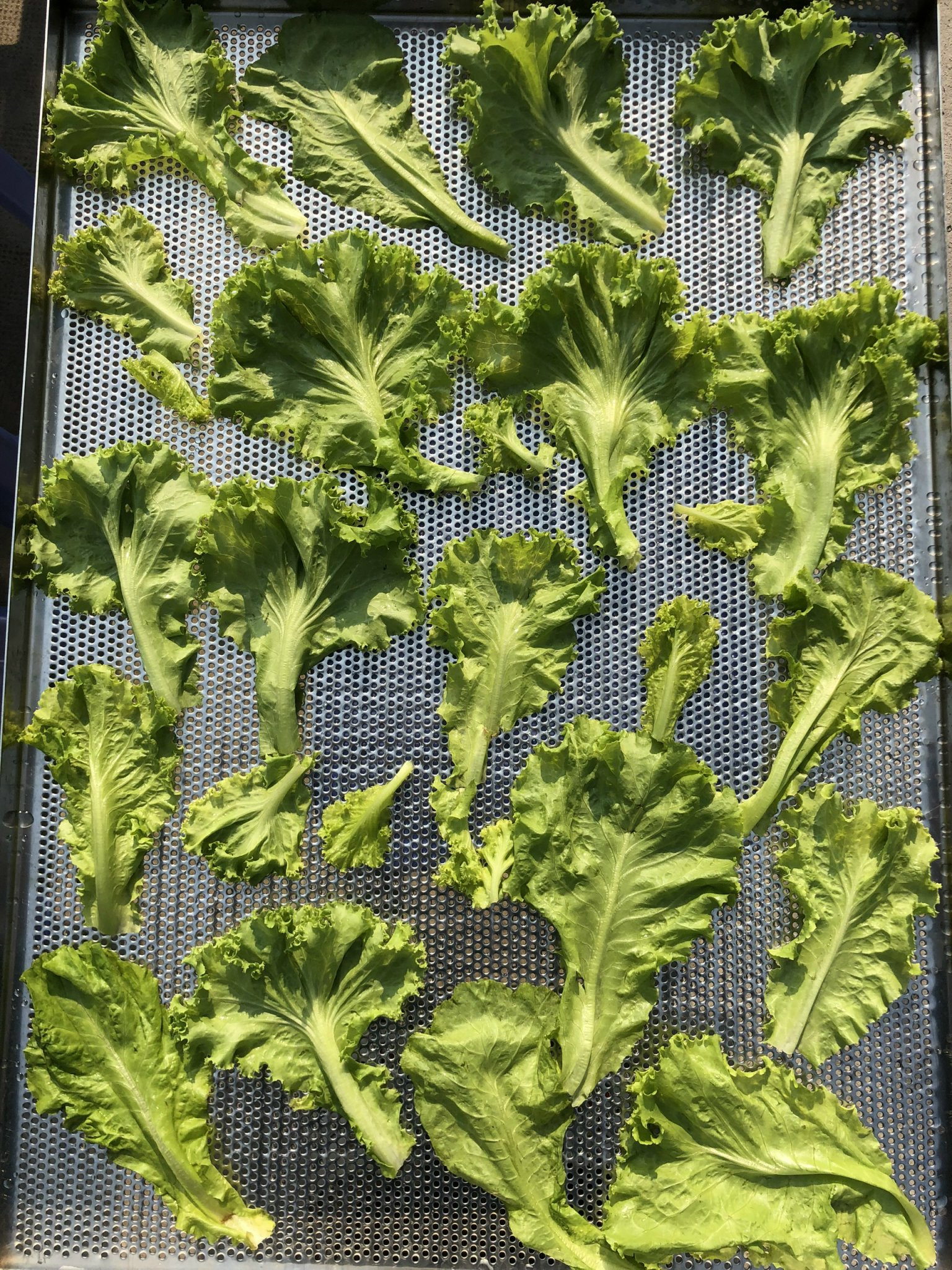

3. Rapid Cooling and Arranging on Industrial Drying Trays
Immediately after blanching, vegetables and fruits are rapidly cooled with cold water or specialized cooling systems to stop the cooking process and preserve their structure. Then, the raw materials are evenly spread on the drying trays of Daxwell industrial dryers or DeAir Heat Pump dryers. Scientific arrangement on trays ensures efficient hot air circulation, ensuring uniform drying for the entire batch.
4. Operating Industrial Dryers and Humidity Control
Vegetables and fruits are dried until they reach the desired crispness, with the final moisture content usually 10% or less. This process is tightly controlled by parameters set on DeAir industrial dehumidifiers or Dezenno industrial rotor dehumidifiers, ensuring an ideal drying environment. The operating principle of the Rotor dehumidifier helps precisely control humidity, preventing mold, which is especially important in cold storage or clean rooms.

DeAir – Your Trusted Partner for Industrial Drying and Humidity Control Solutions
At DeAir, we understand that selecting and operating the right drying equipment, industrial dehumidifiers, or industrial dehumidification systems is a key factor for your business's success. We specialize in providing comprehensive solutions including:
- Daxwell Heat Pump Dryers: Advanced, energy-saving, suitable for drying various agricultural products.
- DeAir & Olmas Industrial Dehumidifiers: Various capacities from large capacity dehumidifiers to dehumidifiers for factories, cold storage for agricultural products, and the food industry.
- Heat Pump Technology: Superior energy savings, ensuring optimal drying and dehumidification performance.
- AHU Systems: AHU (Air Handling Unit) equipment, especially Dezenno.MAX AHU, widely applied in environments requiring strict humidity control such as laboratories or the electronics industry.
Contact DeAir to receive consultation on how to choose an effective industrial dehumidifier, learn about our warranty policy, and explore our professional technical services. We are committed to providing the most optimal solutions for your agricultural product drying and preservation processes!
Sign up for news from DeAir
Related news









![[Case Study] DeAir Installs DeAir.De Rotor Humidity Control System for Pharmaceutical Plant in Binh Duong [Case Study] DeAir Installs DeAir.De Rotor Humidity Control System for Pharmaceutical Plant in Binh Duong](https://deair.com.vn/thumbs/news/2023_04/ban_giao_may_cho_duoc_bd/[270x153-cr]image1-1024x772.jpg__cv.webp)

![[Review & Guide] Olmas OS-300: The New Humidity Control "Warrior" for Medium to Large Warehouses [Review & Guide] Olmas OS-300: The New Humidity Control "Warrior" for Medium to Large Warehouses](https://deair.com.vn/thumbs/news/huong_dan_su_dung_may_olmas_21/[270x153-cr]vtm06440.png)